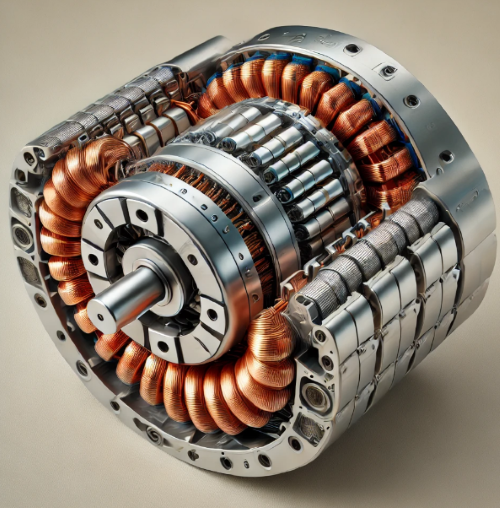
Introduction
Magnets play a crucial role in modern motors, especially in rotor motors, which convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Whether it’s in large industrial motors or small household appliances, permanent magnet rotor motors have become an essential technology across various applications.
What Are Magnet Rotor Motors?
Motors generally consist of two main parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator is the stationary part of the motor, while the rotor is the rotating part. In a magnet rotor motor, permanent magnets are embedded in the rotor, replacing the traditional design that relied on electromagnets.
In this type of motor, the magnetic field generated by the stator interacts with the permanent magnets in the rotor, causing the rotor to spin. This design increases efficiency, reduces energy consumption, and requires less maintenance since the rotor’s magnets don’t need an electrical supply to maintain a magnetic field, unlike electromagnets.

How Do Magnet Rotor Motors Work?
The fundamental principle behind magnet rotor motors is based on electromagnetic interaction. When an electric current passes through the stator’s coils, it generates a rotating magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the permanent magnets in the rotor, creating torque, which drives the rotor to rotate. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Magnetic Field in the Stator: When electricity flows through the coils of the stator, it creates a rotating magnetic field.
- Interaction with Permanent Magnets: The rotating magnetic field from the stator interacts with the permanent magnets in the rotor, either attracting or repelling them, which causes the rotor to spin.
- Continuous Rotation: As the stator’s magnetic field continues to rotate, the rotor is continuously driven, generating mechanical energy.
Since permanent magnets are used in the rotor, there’s no need for additional energy to maintain the rotor’s magnetic field, which leads to higher efficiency.
Benefits of Magnet Rotor Motors
Magnet rotor motors offer several advantages over traditional electromagnetic rotor motors:
- High Efficiency: Since no extra energy is required to maintain the rotor’s magnetic field, magnet rotor motors consume less power, especially under partial load conditions.
- Compact and Lightweight: Due to the high magnetic strength of permanent magnets, especially neodymium magnets, magnet rotor motors can be designed smaller and more compact while still delivering strong power output.
- Low Maintenance: The reduced reliance on complex circuits and brushes, which are typical in electromagnetic motors, leads to less wear and tear, resulting in lower maintenance needs.
- Low Noise: The design of magnet rotor motors allows for less friction and smoother operation, which results in quieter performance—an important feature for noise-sensitive applications.
Applications of Magnet Rotor Motors
Magnet rotor motors are widely used across various industries and devices due to their efficiency, reliability, and energy-saving characteristics. Here are some key application areas:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Most electric vehicle motors are magnet rotor motors. Due to their high efficiency and compact design, these motors deliver powerful performance while maximizing the range of EVs by consuming less energy and producing less heat.
- Household Appliances: In appliances like air conditioners, washing machines, and refrigerators, magnet rotor motors provide more efficient and quieter operation. These appliances often run for extended periods, so energy savings and reduced noise are critical benefits.
- Wind Turbines: The generators in wind turbines often use magnet rotor motors to convert wind energy into electrical energy. The strong permanent magnets help generate electricity more efficiently, especially in low wind conditions.
- Industrial Motors: Magnet rotor motors are used to power machines, pumps, compressors, and other equipment in industrial settings. Their high reliability and low maintenance requirements make them ideal for demanding environments where downtime is costly.
- Aerospace and Defense: Magnet rotor motors are also used in aerospace and defense applications. Their high power density and reliability make them suitable for use in drones, electric aircraft, and military equipment.
Advancements in Magnet Rotor Motor Technology
As technology continues to advance, so do magnet rotor motors. Neodymium magnets have become increasingly popular due to their high magnetic strength, while samarium-cobalt magnets offer better performance at higher temperatures. Researchers are continuously improving motor designs to enhance efficiency, reduce size, and minimize energy consumption. Magnet rotor motors are expected to play an even bigger role in the future of electric vehicles, renewable energy, and other critical sectors.
Conclusion
Magnet rotor motors have become a central technology in modern motor design. Their high efficiency, energy savings, and low maintenance characteristics make them a valuable solution across a wide range of industries, from electric vehicles to industrial machinery and renewable energy systems. For more magnets and magnet assemblies, please check Stanford Magnets.
